- Home
- Steam Resources
- Steam Theory
- Temperature Problems Caused by Air
Basics of Steam
Temperature Problems Caused by Air
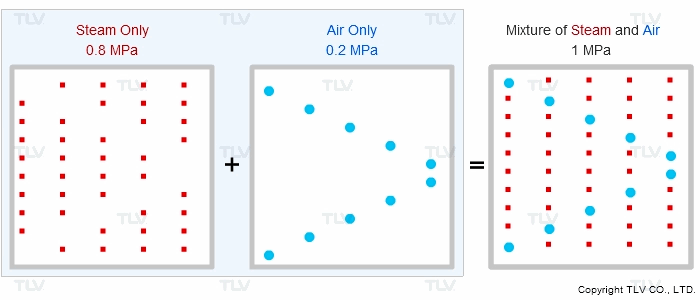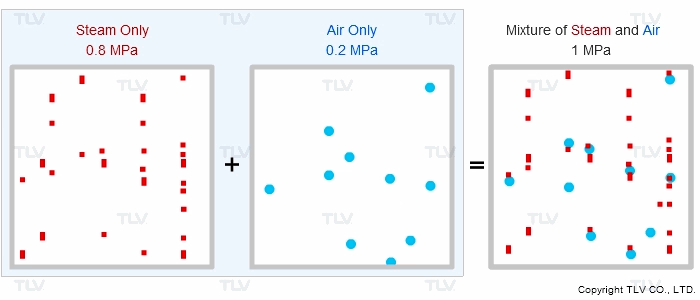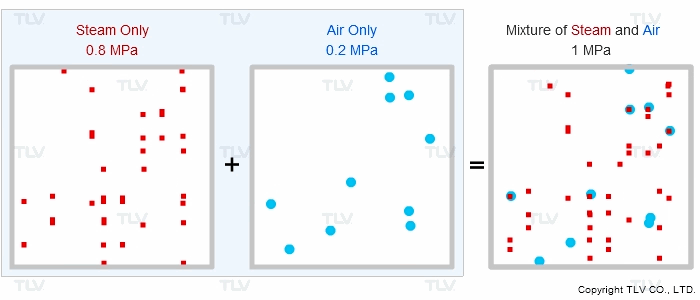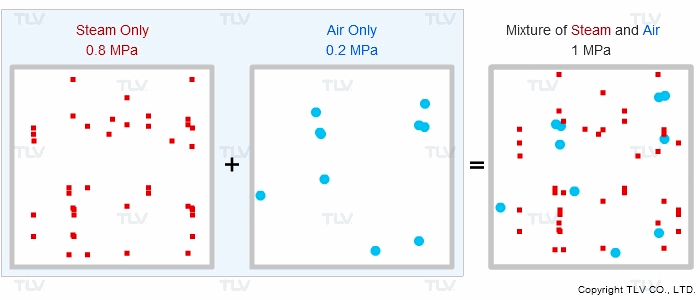
Is the supply steam to your process at the correct pressure, but for some reason under-temperature? Does the product fail to heat up to the correct temperature? Air can diffuse and mix with steam at start-up or during regular operation, which effectively reduces the steam pressure and results in reduced heat transfer. This phenomenon can be explained by Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures.
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
Dalton’s law of partial pressures states that:
“If different types of gas are mixed together, the total pressure of the gas mixture equals the sum of the partial pressures of each type of gas.”
Therefore, if equipment contains other gases in addition to steam, the other gases will affect the total pressure shown on the vessel's pressure gauge.
| Animation of Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures |
|---|
|
|
Why the Temperature Doesn’t Rise
Most types of steam equipment fill up with air when not in use. This air needs be removed from the system at start-up for proper operation. If the air is not removed, the air will stay within the equipment and prevent the steam space from completely filling with saturated steam. When the pressure of the steam space is then measured, the pressure indicated is that of the mixture of air and steam:
When the steam space contains a mixture of steam and air, the pressure indicated by the pressure gauge (PTotal) cannot be used to accurately assess steam temperature, represented byP2.
The actual steam temperature will therefore always be lower than the expected value, which can lead to insufficient temperatures.
Calculating the % Air Mixed with Steam
If you know the temperature within the steam space, the air % by volume can easily be calculated using TLV's online Engineering Calculator.
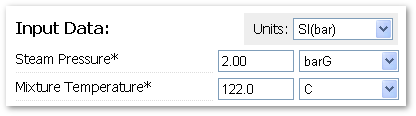
| Engineering Calculator |
|
|
| Simply enter the inlet steam pressure and steam-air mixture temperature to calculate the air % of total volume (as well as obtain the saturated steam temperature). |
Additional Note
Although not directly connected to Dalton's law of partial pressure, it is important to note that air can greatly interfere with heat transfer because it is a poor heat conductor. Air can also cause long start-up times because it restricts steam flow, as well as cause corrosion when it is mixed with water or condensate. In addition, although this article uses the term "air", these problems not only relate to air but also other non-condensable gases such as those that sometimes form as a by-product of water treatment.