- Home
- Steam Resources
- Steam Theory
- The History of Steam Traps #2
Basics of Steam Traps
The History of Steam Traps #2
In The History of Steam Traps Pt 1, we discussed the appearance of several different types of traps throughout the history of traps. The earliest of these was the bucket steam trap, which uses a buoyancy-based mechanical operation principal. After the bucket trap came the thermostatic bimetal trap, whose operation principal relies on differences in fluid temperature. This was followed by the appearance of the thermodynamic disc trap, whose operation principal is based on the phase change of steam -> condensate and the law of energy conservation. In this tutorial, we will discuss which types of traps from each operation principal category are widely in use today and the reasons for their popularity.
Changes in Mechanical Traps
Among mechanical traps, which have the longest history of all trap types, the first to be developed was the bucket trap, which is relatively simple to mass produce. In the bucket traps most commonly used at the beginning, the bucket faced upward ('open bucket') and did not have an attached lever to control the opening and closing of the valve. Instead, most were large traps in which the bucket itself floated up or down to open and close the valve. However, this type of trap soon fell out of use. In contrast, a style of bucket trap in which the bucket was attached to a lever was more widely used. This more compact type of bucket trap, in which the bucket faces downward ('closed bucket'), is still in use today.
Float type traps contain a tightly sealing buoyancy device (float), but the appearance of the float trap had to wait until the processing technology necessary to manufacture the floats was developed. This happened in the years following the appearance of the bucket type trap. As condensate is continually discharged from a float type trap, leaving none to accumulate in the steam process, and the service life of a float trap is relatively long, this type of trap is in the mainstream of traps used today on equipment that requires large discharge capacities.
Changes in Thermostatic Traps
Due to the necessity of both housing a buoyancy device and providing sufficient space for it to operate inside the body, mechanical traps tend to be fairly large. The thermostatic trap was developed in response to the demand for a more compact trap.
The thermostatic trap contains a temperature sensing mechanism. These are sometimes operated by a bellows or a bimetal ring, but whatever the mechanism, all have a very slow response. This sluggish response makes them unsuitable for use on heating processes that require rapid discharge of condensate. For this reason, one thermostatic type trap in use today is a bimetal type temperature control trap designed for steam tracers with a feature that allows the condensate discharge temperature to be set. In response to the drawbacks of the slow response of the thermostatic trap, a balanced pressure type trap whose operation principal utilizes the expansion and contraction of an encapsulated thermoliquid was developed.
Changes in Thermodynamic Traps
In reaction to the thermostatic trap, which though compact has problematically slow response, the thermodynamic trap was developed to meet the need for a trap that allows as little condensate as possible to accumulate.
However, the impulse type that was very common in the beginning had large steam losses, so the disc type developed after that is the type that came into mainstream use. This disc type trap, which is not only compact and versatile but also has the advantage of having a relatively inexpensive initial cost, is the trap type that has been used in the largest numbers in the history of steam traps.
The Continuing Evolution of Modern-day Traps
The three types of steam traps discussed above are still in use today just as described, but what kind of evolution are these modern-day traps undergoing? The evolution of each type of trap focuses on further improving the special features of that particular type of trap.
For example, many of the traps in use today feature an automatic air vent to automatically discharge the initial air at start-up. This feature achieves the aim of reducing both start-up times and the labor involved in valve operation. There are also models of traps for use on equipment that are equipped with high performance automatic air vents to remove hot air during operation.
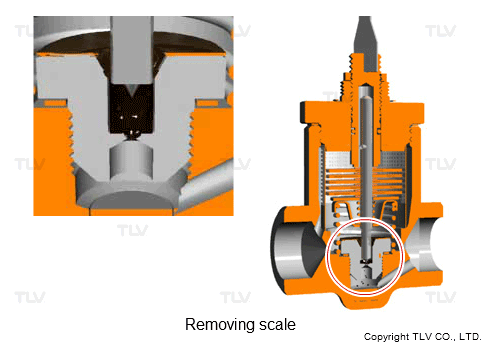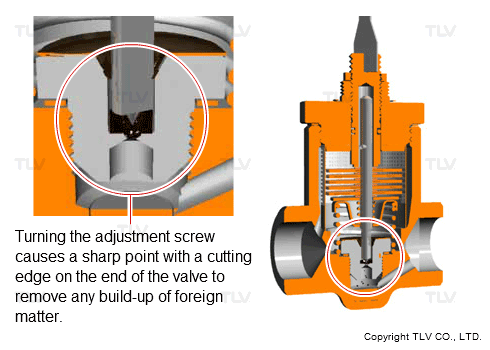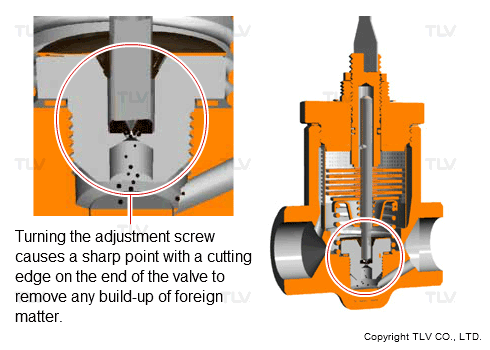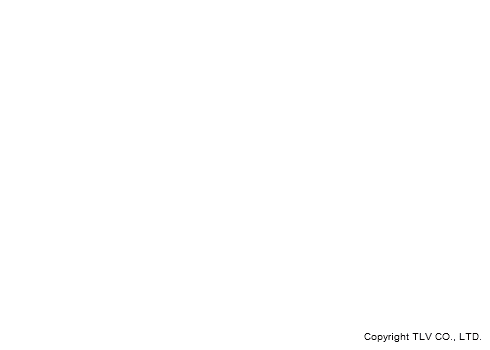
From the standpoint of ease of use, a model has also been developed that has a scale removal function to allow clogs to be removed without the need for disassembly. This feature has made it possible to clear clogs and restore normal operation right then and there as the clogs are found in the course of daily inspections, rather than needing to schedule later disassembly repairs or trap replacements.
In this manner, steam traps are continually evolving in ways that are hidden from sight.
Automatic Air Venting Feature
- Automatic Air Venting using an X-Element
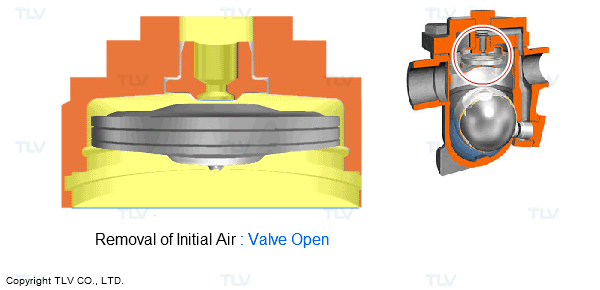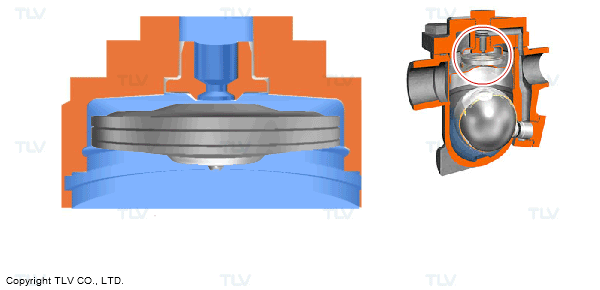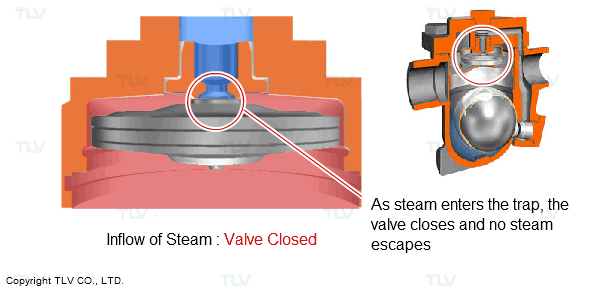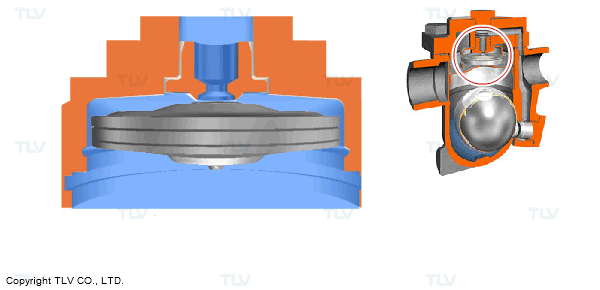
- Automatic Air Venting using a Bimetal Ring

- Scale Removal Function