- Home
- Steam Resources
- Steam Theory
- Trap Back Pressure
Basics of Steam Traps
Trap Back Pressure
What is Back Pressure?
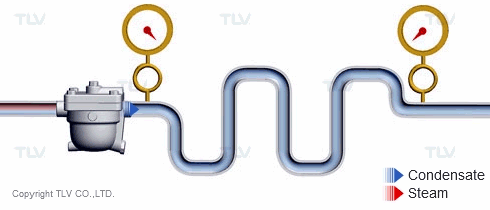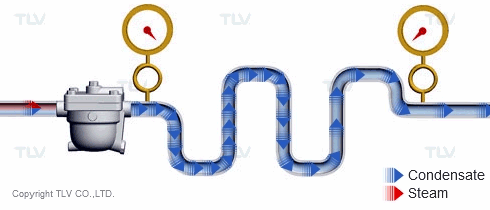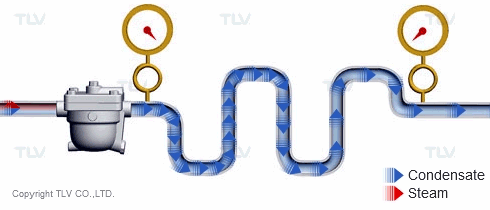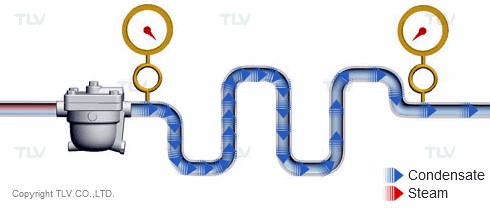
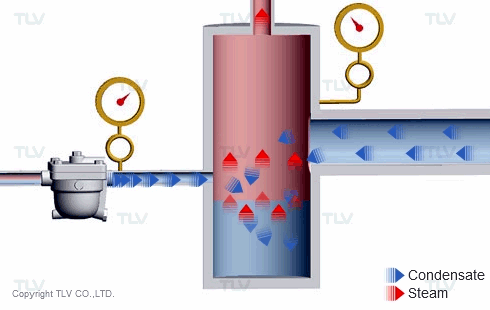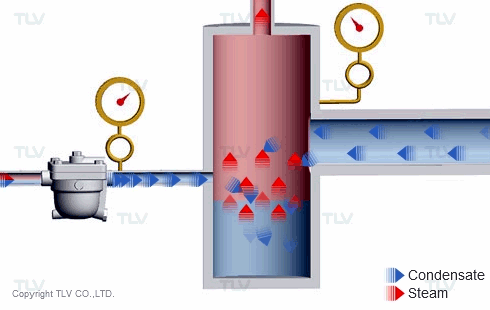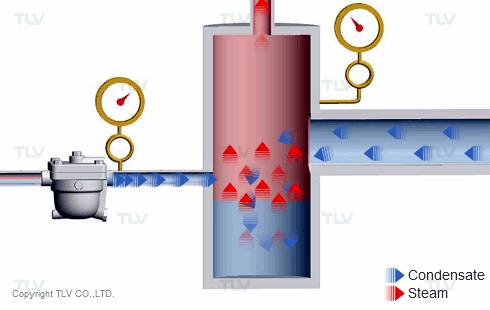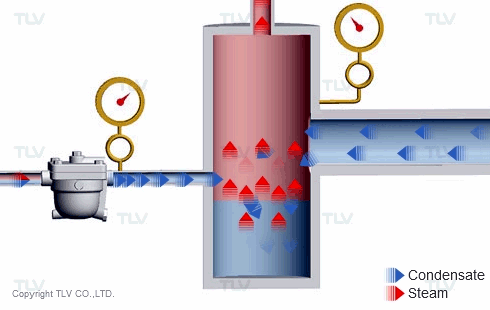
The 'back pressure' is the pressure just downstream of the steam trap. In other words, back pressure is the outlet or secondary pressure of the trap. The difference between a trap's inlet (primary) pressure and back pressure is called the 'differential pressure'.
What Influences Back Pressure?
|
|
| If the condensate is discharged to the atmosphere just after the trap, the back pressure is considered to be 0 MPaG [0 psig]. |
|
|
| Even if the trap discharges to atmosphere, restrictions in the downstream piping such as elbows, tees and valves may add back pressure. |
|
|
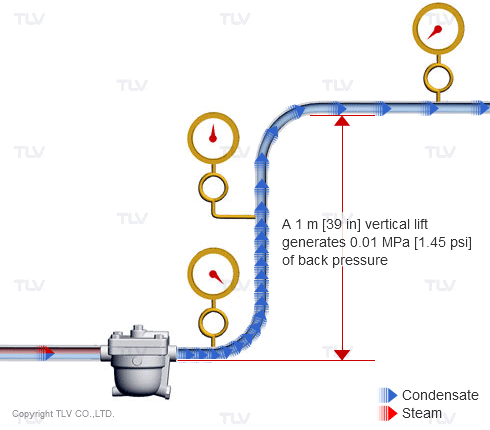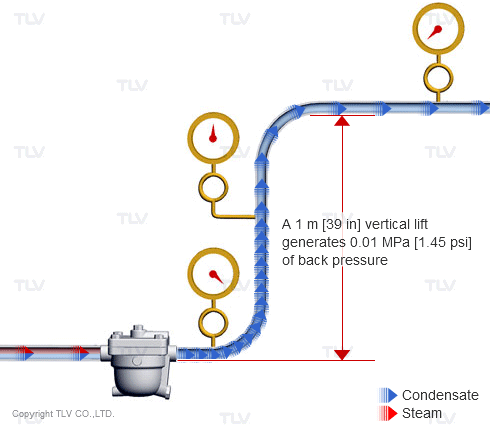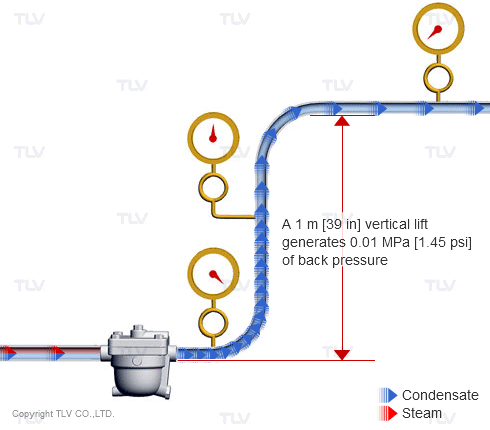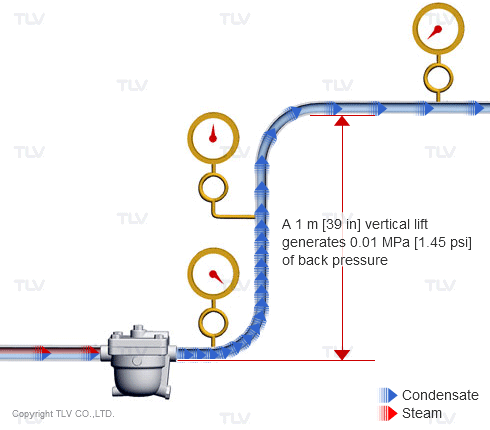
| Vertical lifts (risers) in the condensate piping add back pressure in the form of hydraulic head. |
|
|
| If the condensate discharges into a flash tank and the flash tank pressure increases, the back pressure increases correspondingly. |
Back Pressure and Trap Discharge Capacity
If the inlet (primary) pressure remains stable as the back pressure increases, the trap's differential pressure decreases, which reduces its discharge capacity. Conversely, as differential pressure increases, the trap's discharge capacity also increases.
Maximum Allowable Back Pressure (MABP)
Not only does back pressure influence trap condensate discharge capacity, it can also affect a trap's ability to operate properly. Accordingly, it is also important to consider the maximum allowable back pressure of a steam trap.
A trap's maximum allowable back pressure is the maximum back pressure that the trap can be subjected to and still operate normally. It is usually expressed as a percentage of the trap inlet (primary) pressure.
For thermodynamic disc traps, the back pressure plays a key role in how the trap cycles. As the back pressure increases, the disc valve closure time becomes shorter, and trap's cycle rate becomes faster and faster. At some point, the back pressure may become so high that the trap does not cycle at all and eventually remains open.
Differences in Allowable Back Pressure
The maximum allowable back pressure for disc traps is generally 50% to 80% of the inlet pressure, depending on the product design. So for example, given an inlet pressure of 1 MPaG [145 psig], the back pressure must be less than 0.5 MPaG [73 psig] (if MABP is 50%), or less than 0.8 MPaG [116 psig] (if MABP is 80%). Mechanical traps such as the Free Float® type, on the other hand, have a relatively high MABP of over 90%. Therefore, if the inlet pressure is 1 MPaG [145 psig], Free Float® traps can be used in applications with back pressures exceeding 0.9 MPaG [131 psig].
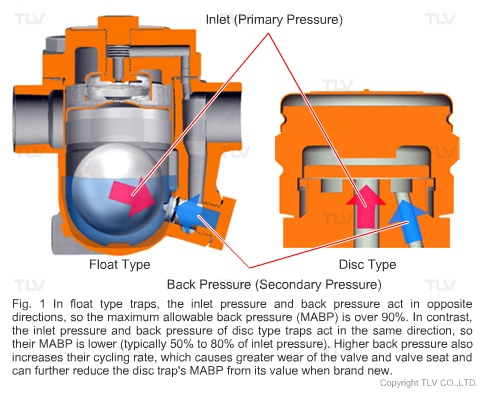
In summary, the maximum allowable back pressure differs depending on the type of trap. When making a trap selection, in addition to considering the condensate discharge capacity, it is also necessary to take into account the back pressure at the planned installation location.
When modifying a system in order to recover condensate from steam traps currently discharging to atmosphere, it is important to determine the back pressure at these traps, and how it will affect both discharge capacity and trap operation.