- Home
- Steam Resources
- Steam Theory
- Heating with Steam
Basics of Steam
Heating with Steam
Steam is one of the most common and effective heat transfer mediums used in industry, but it is not the only medium available. Other fluids such as hot water and oil are also used for indirect heating in heat exchangers. The following series of articles will focus on the advantages of using steam compared to hot water or oil for heating.
Advantages of Steam Heating
Heating with Hot Water or Oil
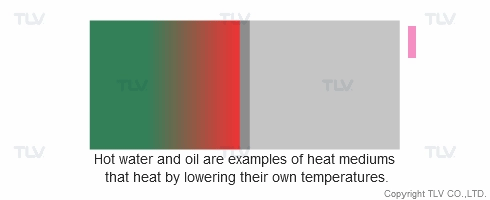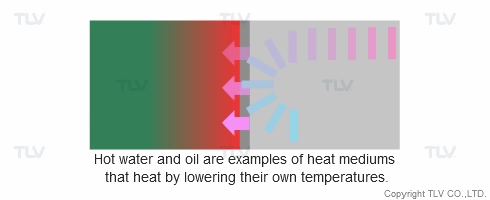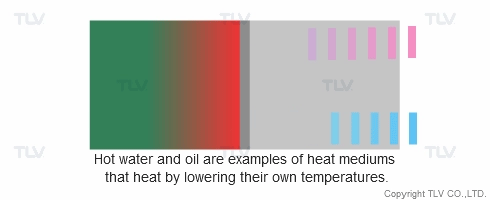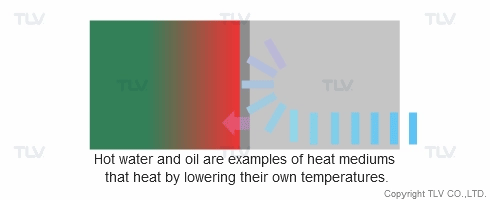
Heat transfer from a liquid medium such as hot water or oil utilizes the medium’s sensible heat. The liquid is supplied at elevated temperatures to the heat exchanger. As the liquid gives off thermal energy, its temperature decreases, exiting the exchanger at a lower temperature. The amount of energy released per unit of heat transfer medium is relatively low (typically around 17 kcal/kg, or 30 Btu/lb).
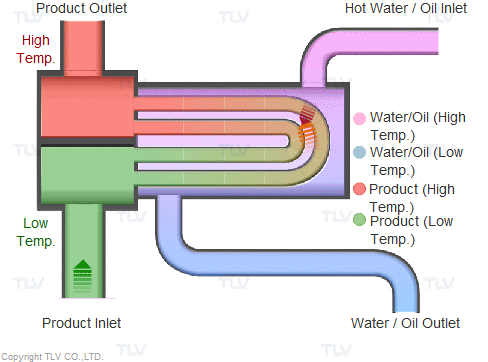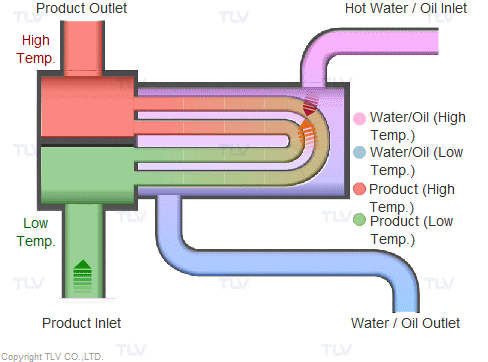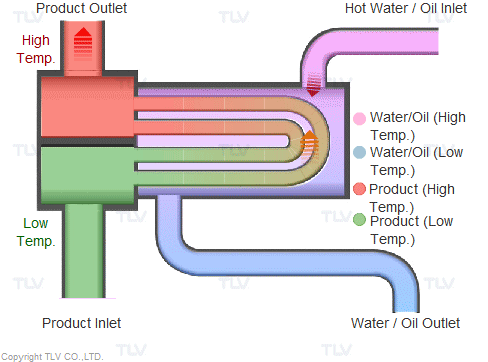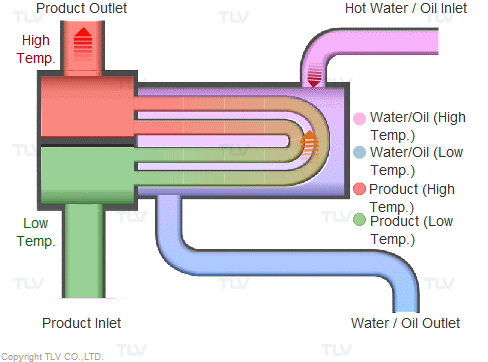
Heating with Steam
Steam is supplied in a gaseous state to the heat exchanger. Heat transfer with saturated steam utilizes the latent heat of steam, releasing a large amount of energy as it condenses (changes to the liquid state). Liquid condensate exits the heat exchanger at close to saturated steam temperatures. The amount of energy released per unit of steam is high (up to 539 kcal/kg, or 970 Btu/lb, and higher with vacuum steam).
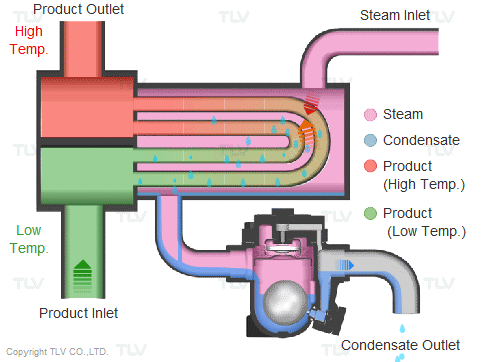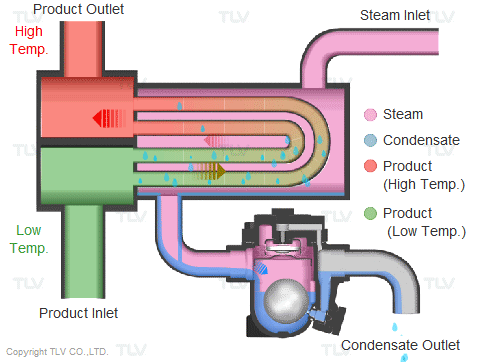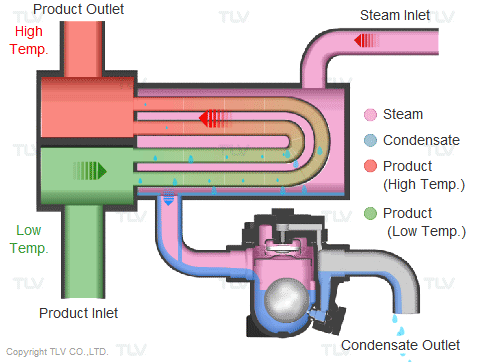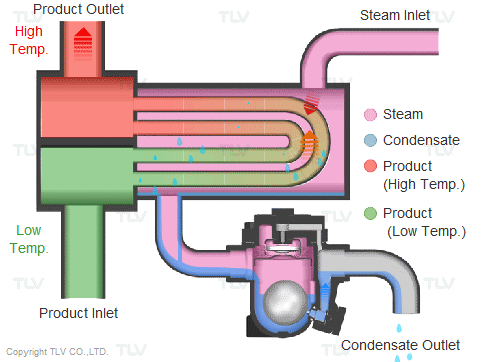

Summary of Benefits
Utilizing latent heat (steam heating) for heat transfer is far more effective than utilizing sensible heat (hot water or oil heating), as a much higher amount of energy is released in a shorter period of time. This offers the following benefits:
| Property | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Rapid even heating through latent heat transfer | Improved product quality and productivity |
| Pressure can control temperature | Temperature can be quickly and precisely established |
| High heat transfer coefficient | Smaller required heat transfer surface area, enabling reduced initial equipment outlay |
To understand the reasons behind these properties and advantages, read the next article on the Steam Heating Mechanism.

